Knee Arthroscopy | Arthroscopy
Benefits | When is it used? | Procedure | Consultation
What is arthroscopy?
Arthroscopy is a joint-preserving operation. An arthroscope, which usually consists of a system of rod lenses, a light source and a rinsing and suction device, is introduced through two small incisions in the joint space. This allows the joint to be examined directly on an external monitor and treated immediately if required. Arthroscopy is used to find out more about changes in the joint, whether they are degenerative (joint wear), inflammatory, traumatic (caused by an accident) or tumorous, and thus determine the right post-operative treatment. Arthroscopy can also be used as a treatment method for minor damage and injuries.
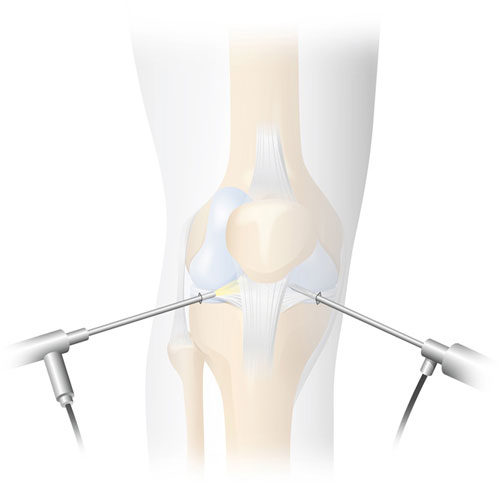 Arthroscopic procedures can be performed on all joints. They are commonly used on the knee, shoulder and ankle joints, and less often on hips, elbows and other joints.
Arthroscopic procedures can be performed on all joints. They are commonly used on the knee, shoulder and ankle joints, and less often on hips, elbows and other joints.
Arthroscopy is minimally invasive surgery, which is often performed for minor injuries. Arthroscopy has the following benefits over open surgical procedures:
- Lower stress on the body
- Less pain after the procedure
- Shorter regeneration/healing times
- Faster return to day-to-day activities
Arthroscopy is required if the previous conservative treatment (medication, physiotherapy, etc.) has not provided satisfactory relief. It can be indicated for the following conditions:
Arthroscopy will slow the progression of osteoarthritis considerably, but in most cases it provides only temporary relief. Usually the pain of osteoarthritis returns faster than expected. In addition, many patients who have waited too long to get treatment due to their fear of surgery already have considerable functional impairment and malpositioning of the knee joint (bow legs or knock knees), so arthroscopy may no longer be possible as a treatment for osteoarthritis. In many cases, relief of the symptoms of osteoarthritis and restoration of mobility can only be achieved through artificial knee joint resurfacing (i.e. a knee replacement).
Depending on the particular problem, arthroscopy usually takes between 45 and 90 minutes. First, the optical instruments are inserted through small incisions and the surgical area is assessed. Then, for example, the cartilage can be smoothed and any torn tissue (e.g., meniscus) can be removed or sutured.
Depending on what surgery is performed, arthroscopy can be either an outpatient or inpatient procedure. This is arranged in advance with the insurance provider.
Arthroscopy is a common, routine procedure, with very few adverse events or complications. Nevertheless, it is important to understand that the following problems and complications cannot be completely ruled out: infection, thrombosis, joint or nerve injuries.
Our doctors have many years of experience and are highly skilled in sports and joint surgery. Dr Andreas L. Oberholzer is a well-known expert in knee surgery and has extensive experience in knee replacements. He trains international doctors in this area and supports the further development of soft-tissue-oriented techniques for the implantation of artificial knee joints. You can find out more about his work here.
We guarantee rapid, expert assessment and consultation and treatment in line with the latest medical findings. Don’t hesitate to get in touch if you would like a second opinion.